What is the product development process?
A Product Development Process refers to all of the processes that a company must accomplish to take a product from conception to the point it is made available.
For example, the process often entails identifying a need in the industry, performing market research to identify and qualify a potential opportunity, developing a product roadmap, and designing and building an initial minimum viable product (MVP).
Who is responsible for the Product Development Process
The Product Manager may be the most critical function in the entire product development process. Given that they are ultimately accountable for the success of a company’s products, they are typically the driving force behind the development of those items.
The Product Manager’s responsibility is broad, as it is they who will bring together the many departments of the organization, use the product roadmap to promote strategic objectives, and have overall control over the operations of the development team.
Preparation For the Product Development Process
Preparation for the market It is necessary to adopt many strategies to prepare the product for entry into the marketplace. These strategies include sourcing materials, scaling, distribution networks, pricing points for the product, and developing a product launch plan. All parts of your company and product team will compile all financial, marketing, and sales documentation together.
After then, the product will be released into the marketplace for purchase. The stages of development may overlap depending on the product and the nature of the business. It is often more efficient to begin a phase before the preceding one has concluded, although the stages are typically started sequentially and interdependent. Market preparation, for example, might start even before the product has been fully designed and manufactured.
The Phases of a Product Development Process
Product development can occur in various ways, each with its own unique set of requirements. The following are more general concepts that tend to appear in each scenario and are universally accepted:
Idea: This is the stage of the business cycle where ideas are harvested. An Idea Management System, with specific routes in place to collect ideas from the organization’s employees may even be at the organization’s disposal. The alignment of the concept with the business’s strategic objectives will, without a doubt, be an essential topic that is considered. You will abandon the idea if it does not and cannot be modified to achieve those objectives.
As a part of this phase, you will work up financial allocations for distinct product strands, staff resources and tasking designations will be worked out, you will create product requirements, and engineering methodologies will be described.
This is when the product transitions from being primarily conceptual to becoming more concrete. Development This is the only area where the development team is allowed to be.
Definition: It’s time to define the product once you’ve finished the business case and addressed your target market and product functionality. This process, also known as scoping or idea development, focuses on fine-tuning the product strategy.
Making a prototype: During the prototype stage, your team will conduct extensive research and documentation on the product while developing a complete business strategy and building it.
These early prototypes might be as simple as a sketch or as complicated as a computer rendering of the first idea. These prototypes assist you in identifying areas of risk before developing the product.
Furthermore – Various operations will be performed in the product’s development, including framework development and dependency planning, sprints, project strand merging, quality assurance, and other similar activities. You, your management, or your product team may conduct beta testing to evaluate the product in a real-world context and collect input from consumers and the market.
A prototype may also be made available to those who are interested. As the project proceeds, it is excellent if technical documentation relevant specifically to the product is being developed.
Intel designing: Project stakeholders collaborate to create a mockup of the product based on the MVP prototype during the early design phase. The design should be made with the target audience in mind and complement the product’s primary purposes.
Keep in mind that It may take multiple iterations to perfect a great product design, and it may also need communication with distributors to get essential materials.
Examination: You must first validate and test a new product before it can go live. This assures that all aspects of the development, from creation to marketing, are in good operating order before being made available to the general public.
Going commercial: It’s now time to market your idea, which entails releasing your product and putting it on your website.
Suppose you got this far – congratulations! You’ve finished the design and put your development and marketing plan through its Phrases. It would help if you were comfortable with your final iteration and prepared to deliver your final result.
How To Use Product Development Process
Various frameworks have been developed to help companies produce products for their customers. Using one of them is a wise move to get things started.
As an idea progresses through the development process from concept to reality, the complexity of the product development process increases. Maintaining efficient oversight and delivery of the project requires a framework, which you, as a manager, must follow.
The IDEO technique, the BAH model, the Stage-gate model, the Lean Start-up strategy, and the Exploratory Product Development approach are some examples of concepts.
Following are some key elements you should take into consideration to perform a well-put product development process:
Understanding and attitude of the consumer
When an idea is conceived, it could have come about by any means, from a single flash of insight by a single person to the collaboration of numerous groups based on a need in the market. In any case, having a thorough understanding of the attitudes and behaviors of the product’s customers is a significant asset.
Whenever possible, integrating consumer intelligence into the development process will help maintain the product relevant and market-fit throughout the development process, from early idea validation to real-world beta testing later in the development process.
The invention of new concepts
Consider ideas from any part of the organization’s workforce and keep an open mind. A company’s success is dependent on a constant flow of new ideas.
Furthermore, any team member may come up with an idea for a fantastic product, and eliminating any individuals or groups may result in the loss of a lucrative commercial opportunity. It is possible to ensure that no chances are missed by establishing an initiative or a system to collect ideas throughout the entire organization. This will also help the workforce to feel more fulfilled and motivated.
Communication
Maintain the viability of internal communication channels inside the organization. This is so that expertise and knowledge may be easily transferred from person to person, between teams, across departments, and throughout the organization.
Timelines and deadlines
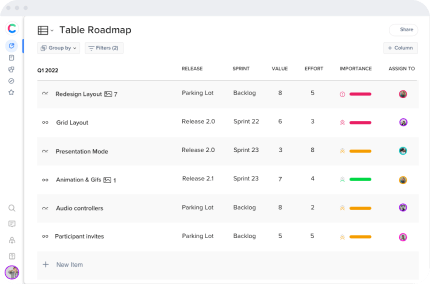
When establishing development timelines, be reasonable and pragmatic in your expectations. The use of product roadmaps to guide the evolution of a product can aid in the creation of efficient work schedules.
Using these can also assist in prioritizing and sequencing the appropriate initiatives and understanding the relationships between the project’s dependencies and dependencies on other industries.
Conclusion
It might be challenging to bring a new product to life. You know you have a concept that can benefit a target market, but you’re not sure how to get your product in front of them.
Keep in mind: The product development process can be insensitive if you’ve never done this before since you may not know where to begin.
Typical weaknesses of many businesses and difficulties like missed opportunities, accumulated technical debt, a failure to share innovation, poor mentoring, and poor leadership.
Thankfully, there is a blueprint for new product creation, which is a plan that will assist you in bringing your ideas to reality.