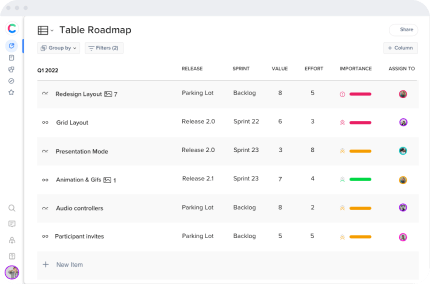
Sales forecast
A sales forecast (SF) assesses a product’s expected sales. A sales forecast will estimate how much your business expects to sell a specific product in a predetermined period. A sales forecast is measured mainly by how well it succeeded in forecasting the current sales. A sales forecast is an estimate of future product sales made based on several criteria, such as past sales data, economic trends, and the performance of competing brands.
The importance of Sales Forecasts
A sales forecast enables organizations to make informed decisions about everything from allocating budgets to arranging workforces to managing resources and everything in between. Furthermore, your decision-making process can be open to high risks in terms of real estate investment without a well-put sales forecast. For example, if a particular product has a very high SF, the company should prepare a high stock to answer the demand. Without knowing that, you are most likely to have serious inventory problems that could damage your sales and reputation.
The advantages of Sales Forecasting
A sales forecast enables organizations to make informed decisions about everything from allocating budgets to arranging workforces to managing resources and everything in between. Furthermore, a good SF will guide you through the day-to-day decision-making process in various areas, such as which projects to pursue and which to abandon. How much money to put into inventory, where to get funding for a marketing campaign, etc.
Sales Forecasting for Startups vs. Sales Forecasting for Established Businesses
Startups may find sales forecasting more challenging than established businesses with years of expertise under their belt. Indeed, they will have access to historical sales data and audience insights. In contrast, newcomers will rely on more general market research and rival analysis to predict their potential sales.
How to Make Use of Sales Forecasts
Businesses can use the approaches listed below to create a compelling sales forecast for their company:
Define Your Sources of Income (revenue streams)
Companies must identify and categorize their revenue sources and segment their products depending on important aspects (type, demographics, etc.). Split down your income streams as much as possible to correspond to your accounting setup; this will make it easier to assess the gap between predicted and actual revenue later on.
Make Use of Historical Data
Historical sales data is an essential resource when a company attempts to make a sales forecast for the first time. Make an effort to maintain previous data in context and consider economic conditions and trends.
Keep in mind that just because one product line performed well two years ago does not guarantee that another similar product will perform similarly in the future — you may introduce them into a completely different environment.
Compare and Contrast The Product With Others
Selling a new product can be difficult, and evaluating the performance of similar products, particularly those produced by competitors, might help to alleviate some of the difficulties.
Although the sales estimate generated may not be as accurate as possible, it can still help organizations make profitable decisions.